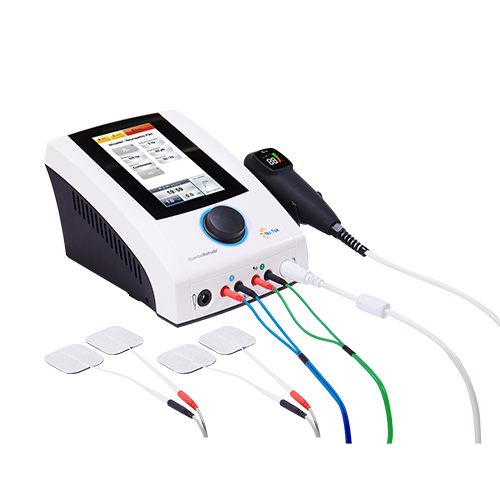
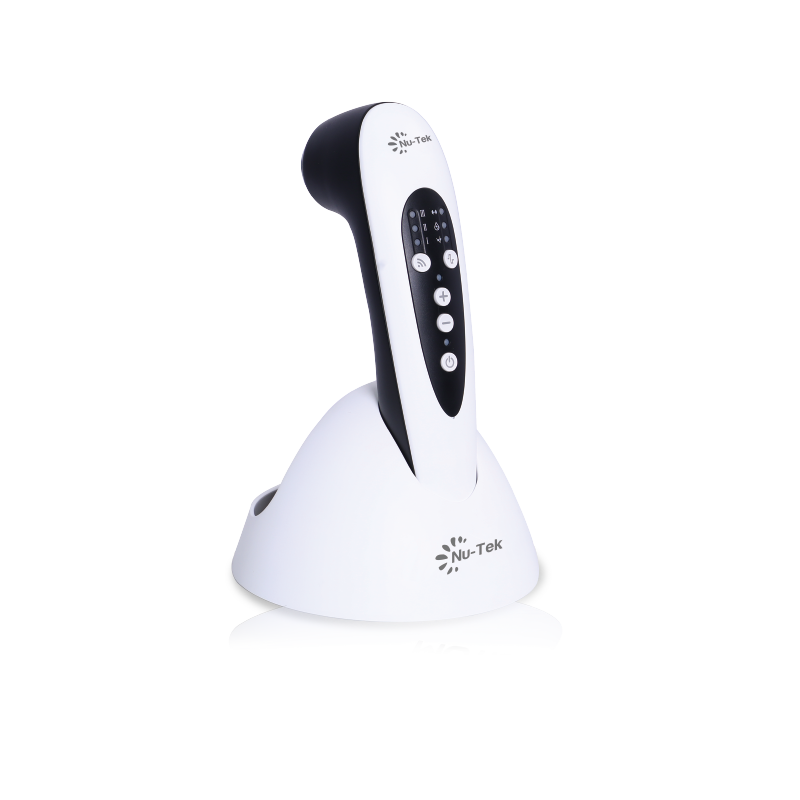
Magnetotherapy is a therapeutic technique that utilizes magnetic fields to promote healing and alleviate pain. This modality is based on the application of static or pulsed magnetic fields to various parts of the body. Magnetotherapy is used in physical therapy, rehabilitation, and alternative medicine to treat a variety of conditions.
What is Magnetotherapy?
Magnetotherapy involves the use of magnets or devices that generate magnetic fields. These fields can be applied through various methods, including:
Static Magnets: These are permanent magnets that can be placed on or near the body.
Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields (PEMF): This involves devices that generate changing magnetic fields. PEMF therapy can be more versatile and is often used in clinical settings.
How Does It Work?
Mechanism of Action:
Cellular Interaction: Magnetotherapy is thought to influence the electrical charges and ion exchanges within cells, potentially affecting cellular metabolism and communication. This can lead to improved cellular function and enhanced healing.
Increased Blood Flow: The application of magnetic fields may promote vasodilation (the widening of blood vessels), improving blood circulation to the treated area. This increased blood flow can help deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues while facilitating the removal of metabolic waste.
Reduction of Inflammation: Magnetic fields can have anti-inflammatory effects, helping to reduce swelling and pain associated with inflammatory conditions.
Pain Relief: Magnetotherapy may modulate pain perception by affecting the nervous system. It can influence the release of neurotransmitters and endorphins, leading to a reduction in pain sensitivity.
Effects on Pathology
Magnetotherapy is used to address various health conditions, including:
Musculoskeletal Pain:
Conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and lower back pain can benefit from magnetotherapy by alleviating pain and improving joint function.
Soft Tissue Injuries:
Magnetotherapy is often used for treating sprains, strains, and tendonitis. It can promote healing by enhancing blood circulation and reducing inflammation in the affected tissues.
Chronic Pain Syndromes:
Patients with chronic pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia, may find relief through magnetotherapy by reducing pain and improving overall well-being.
Wound Healing:
Magnetotherapy can enhance the healing process of chronic wounds and ulcers by stimulating blood flow and promoting tissue regeneration.
Neuropathy:
Conditions like diabetic neuropathy may respond positively to magnetotherapy, helping to alleviate symptoms and improve nerve function.
Post-Surgical Recovery:
Following surgery, magnetotherapy may aid in reducing pain and swelling while promoting faster healing of the surgical site.
Stress and Anxiety:
Some studies suggest that magnetotherapy can have a calming effect and may be beneficial in reducing stress and anxiety levels.
Improvement in Sleep Quality:
Magnetotherapy may help improve sleep quality by promoting relaxation and reducing discomfort.
Magnetotherapy is a non-invasive treatment modality that utilizes magnetic fields to promote healing, reduce pain, and enhance overall well-being. Its mechanisms are thought to involve improved cellular function, increased blood flow, and anti-inflammatory effects, making it suitable for a variety of musculoskeletal and soft tissue conditions. As with any therapeutic intervention, patients should consult with healthcare professionals to determine the appropriateness of magnetotherapy for their specific conditions and to develop an effective treatment plan

 中文
中文 Español
Español Français
Français Português
Português
