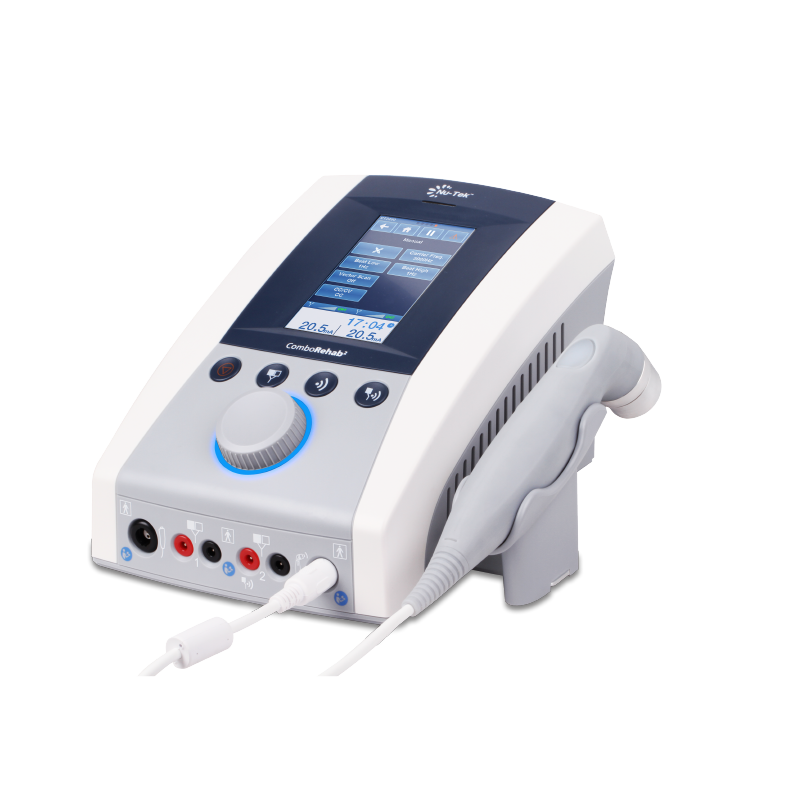
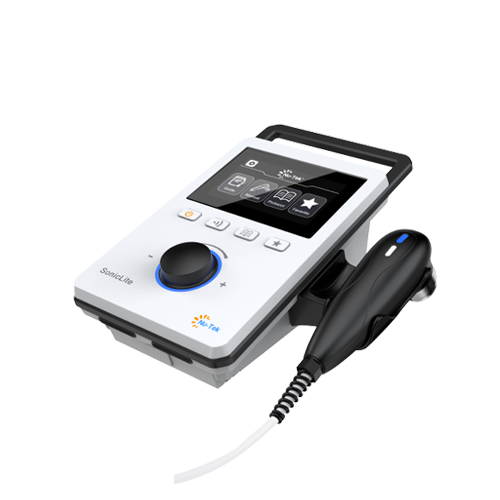
Shockwave therapy, also known as extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), is a non-invasive treatment that utilizes acoustic waves to promote healing and reduce pain in various musculoskeletal conditions. This therapy has gained popularity in physical therapy, sports medicine, and orthopedics due to its effectiveness in treating chronic pain and facilitating recovery from injuries. Here’s a detailed overview of shockwave therapy:
How Shockwave Therapy Works
Generation of Shockwaves:
Shockwave therapy generates acoustic waves that are delivered to the affected area of the body. These waves are produced by a device that creates high-energy pulses, which travel through the skin and into the underlying tissues.
Types of Shockwaves:
Radial Shockwaves: These are low-energy waves that spread out from the source. They are commonly used for surface-level treatment and are effective for conditions like plantar fasciitis and tendonitis.
Focused Shockwaves: These are high-energy waves that converge at a specific point, allowing for deeper penetration into tissues. They are used for more severe or deep-seated conditions, such as calcific shoulder tendinopathy or deep tissue injuries.
Mechanism of Action:
Shockwaves stimulate cellular processes, promoting tissue repair and regeneration. The therapy helps in:
Increased Blood Flow: By stimulating circulation, shockwave therapy enhances nutrient delivery to the affected tissues.
Reduction of Pain: It alters the pain perception pathway by desensitizing nerve endings in the treated area.
Breakdown of Calcium Deposits: In cases of calcific tendonitis, shockwaves can help break down calcifications, facilitating their absorption and improving mobility.
Indications for Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave therapy is commonly used to treat a variety of musculoskeletal conditions, including:
Tendinopathies:
Conditions such as Achilles tendinopathy, patellar tendinopathy (jumper’s knee), and tendinitis in the shoulder or elbow (e.g., lateral epicondylitis).
Plantar Fasciitis:
Effective in relieving pain associated with this common condition that affects the heel and bottom of the foot.
Calcific Shoulder Tendinopathy:
Helps dissolve calcium deposits in the shoulder joint, reducing pain and improving range of motion.
Trigger Points:
Addresses myofascial pain syndrome by targeting trigger points in muscles to reduce pain and tension.
Fractures:
Can be used to promote healing in non-union fractures or stress fractures that are slow to heal.
Pain Management:
Used in various chronic pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia or chronic low back pain, to improve quality of life.
Procedure
Preparation:
A healthcare professional evaluates the patient’s condition and determines the suitability of shockwave therapy. The area to be treated is identified.
Application:
The patient typically lies down, and a conductive gel is applied to the skin over the targeted area to facilitate the transmission of shockwaves.
The shockwave device is placed on the skin, and the treatment is initiated. The duration of the session usually lasts between 15 to 30 minutes, depending on the condition.
Post-Treatment Care:
Patients may experience some soreness in the treated area, which usually subsides within a few days. Minimal downtime is required, and many patients can return to their daily activities immediately after treatment.
Benefits of Shockwave Therapy
• Non-Invasive: Provides an alternative to surgery and more invasive treatments.
• Minimal Side Effects: Generally well-tolerated with few adverse effects; potential side effects include transient soreness or swelling.
• Rapid Recovery: Patients often experience relief within a few sessions, and many report significant improvement in pain and function.
• Versatility: Effective for a wide range of conditions, making it a valuable tool in rehabilitation and pain management.
Limitations and Contraindications
While shockwave therapy is effective for many patients, it may not be suitable for everyone. Some contraindications include:
• Pregnancy: Avoidance of treatment over the abdomen or pelvic region.
• Active Infections: Treatment should not be applied over infected tissues.
• Tumors or Malignancies: Should not be used on cancerous tissues.
• Severe Vascular Disorders: Conditions that impede blood flow may not respond well to therapy.
• Pacemakers or Other Electronic Implants: Caution is advised in these cases.
Shockwave therapy is a promising and effective non-invasive treatment option for various musculoskeletal conditions. It leverages the power of acoustic waves to stimulate healing, reduce pain, and improve function. As with any medical treatment, it's essential for patients to consult with a qualified healthcare provider to determine if shockwave therapy is appropriate for their specific condition and to develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
Radial shockwave therapy (RSWT) is a form of extracorporeal shockwave therapy that uses low-energy acoustic waves to treat various musculoskeletal conditions.

 中文
中文 Español
Español Français
Français Português
Português